
Audio signals can be compressed based on audio compression technology.
Audio compression technology refers to the use of appropriate digital signal processing techniques for the original digital audio signal stream (PCM encoding) to reduce (compress) its code rate without loss of useful information or negligible loss. It is called compression coding. It must have a corresponding inverse transform called decompression or decoding. Audio signals may introduce a large amount of noise and certain distortion after passing through a codec system.
In the field of audio compression, there are two compression methods, lossy compression and lossless compression. Commonly known MP3, WMA, and OGG are called lossy compression. As the name implies, lossy compression reduces the audio sampling frequency and bit rate, and the output audio file will be smaller than the original file. Another type of audio compression is called lossless compression, which is the subject matter to be said. Lossless compression can compress the volume of the audio file less than 100% of all the data of the original file, and restore the compressed audio file to achieve the same size and the same code rate as the source file. The lossless compression formats are APE, FLAC, WavPack, LPAC, WMALossless, AppleLossless, La, OpTImFROG, Shorten, and the common, mainstream lossless compression formats are APE and FLAC.
Audio compression technology coding classificationCoding : How the signal system contains certain information content in a combination of a small number of specific signals
1, using a certain format to record digital data
2, using a certain algorithm to compress digital data to reduce storage space and improve transmission efficiency
Audio signal coding is divided into waveform coding, parameter coding and coding modes of various technologies according to the compression principle.
Waveform coding
The time domain or frequency domain waveform of the audio signal is directly sampled at a certain rate, and then the amplitude sample is hierarchically quantized and converted into a digital code, and a reconstructed signal is generated from the waveform data.
The coding system is derived from the original signal value, and the waveform and the original sound waveform are as close as possible, retaining the details of the signal and various transition characteristics.
Waveform coding type
Pulse code modulation (pcm) → differential pulse code modulation (dpcm) → adaptive differential pulse code modulation (adpcm)
Pulse code modulation (PCM)
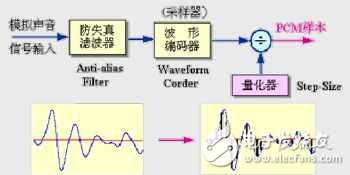
The simplest waveform coding, just sampling and quantifying the input signal
The sound bandwidth is limited by the sampling frequency, and the sampling frequency and signal bandwidth are matched by an anti-aliasing filter.
Using non-uniform quantization, a large quantization interval is used for the input signal with a large amplitude, and a small quantization interval is used for the input signal with a small amplitude, and the signal is represented by a small number of bits when the quantization precision is satisfied.
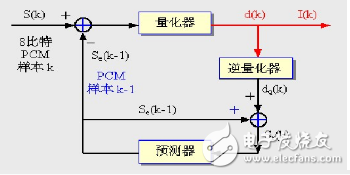
Differential Code Modulation (DPCM)
From the PCM, according to the sound sample, the adjacent sample values ​​show obvious correlation, and the previous sample is used to estimate the amplitude of the next sample signal to form the predicted value.
Quantify the difference between the predicted sample value and the original sample value
If the predicted value of the sample is close to the actual value of the sample, the change in the magnitude of the difference between the samples is smaller than the change in the amplitude value of the original sound sample, so that the quantized signal can be quantized with a smaller number of bits. Representation difference
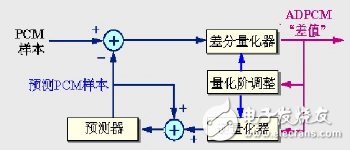
Adaptive Differential Coded Modulation (ADPCM)
Combining the adaptive and differential characteristics of the quantization step size according to the magnitude of the input signal, the core idea is:
Use small quantization levels to quantify small differences and large quantization levels to quantify large differences
Estimate the predicted value of the next sample using the past sampled sample values ​​so that the difference between the actual sample value and the predicted value is always the smallest
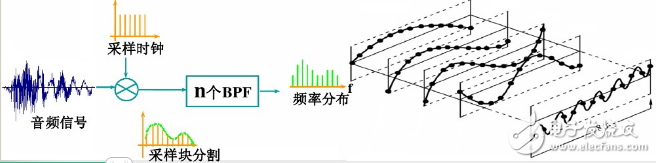
Subband coding (SBC)
Frequency domain coding based on perceptual characteristics
The audio signal is segmented for a short enough time to be converted from the time domain to the frequency domain by the segmentation block, and the band of the original signal is divided into several subbands by a band pass filter (BPF) group.
For sub-bands where auditory perception is more important, the encoder assigns more bits to represent them. For other sub-band encoders, fewer bits can be assigned to represent
Adaptive control of different sampling frequencies and different quantization intervals by using audio signals in each sub-band due to different sub-band frequency ranges
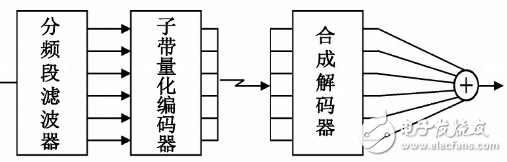
Set m-channel digital encoder when transmitting on the channel, combine the codes of each sub-band and output the sub-band encoded data through the multiplexer.
The sub-band output signals are sent to the m-channel parallel digital decoding, and the synchronization is added, and the addition is restored to the original signal.
Adaptive Transform Coding (ATC)
Transform coding is a function transformation of a signal, transforming from one signal (space) to another (space), and then encoding the signal.
Most of the audio signals are low-frequency signals. The energy of the signals in the frequency domain is concentrated. By transforming the time-domain signals into the frequency domain and then sampling and encoding, you can definitely reduce the data.
The most common transform coding is the application of discrete cosine transform (DCT) or modified discrete cosine transform (DCT).
The transform coding process is to sample the audio signal for a short enough time, and transform the time domain into a frequency domain through the sample block. The function of the sample block is equivalent to presenting continuous audio in a “window†for processing.
In the transform system, the total number of bits used to quantize a set of transform samples is fixed, so by selecting the length of the transformed sample block (window), the time domain resolution and the coding compression ratio can be adjusted, and the short sampling block can be improved. Time domain resolution, long sample block can achieve higher compression ratio
The concept of self-adaptation is mainly reflected in the acoustic psychology model. The sampling block (window) length is switched according to the characteristics of the audio signal, and the conflict between the time domain resolution and the coding compression ratio is alleviated.
Both transform coding and subband transformation work for a certain sample block. Subband coding has excellent time resolution but poor frequency resolution. Transform coding has excellent frequency resolution, but time resolution is poor.
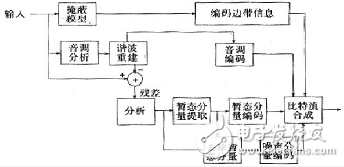
Parameter coding
Firstly, the feature model is established according to different signal sources, such as language signal and natural sound. By extracting the feature parameters and coding process, the reconstructed sound signal is kept as high as possible to maintain the semantics of the original sound, but the waveform of the reconstructed signal is the same. The waveform of the sound signal may vary considerably.
Commonly used characteristic parameters include formant, linear prediction coefficient, band division filter and other parameter coding techniques to achieve low-rate sound signal coding, and the bit rate can be compressed to 2Kbi/s-48Kbi! s, but the quality of the sound can only reach medium, especially the low degree of naturalness, only suitable for the transmission and expression of language
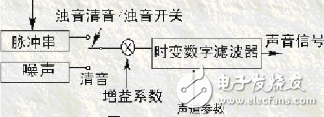
Mixed coding
A coding form that combines waveform coding and parametric coding
Overcoming the weaknesses of the original waveform coding and parametric coding, trying to maintain the high quality of the waveform coding and the low rate of the parametric coding, and obtain high quality synthetic sound signals at 4-16 Kbit / s rate.
The basis of hybrid coding is linear predictive coding (LPC), commonly used pulse-excited linear predictive coding (MPPPO), and planned pulse-excited linear predictive coding (KPELPO) codebook-excited linear predictive coding (CELPO).
Led Floor Panels,Led Dance Floor Panel,48W Led Light Panel,Floor White Uplight Panel Led
Kindwin Technology (H.K.) Limited , https://www.szktlled.com