 In your application, the Hall-effect sensor is more modern and the reed switch sensor will remain the best choice. Since introducing the Hall-effect sensor several years ago, it won the designer's design imagination, generally considered the solid-state device ratio Mechanical and electronic devices are more reliable. However, when comparing the reed sensor technology with Hall sensor technology, some noteworthy advantages can be observed.
In your application, the Hall-effect sensor is more modern and the reed switch sensor will remain the best choice. Since introducing the Hall-effect sensor several years ago, it won the designer's design imagination, generally considered the solid-state device ratio Mechanical and electronic devices are more reliable. However, when comparing the reed sensor technology with Hall sensor technology, some noteworthy advantages can be observed. Reed sensor technology The key component in the reed sensor is the reed switch, which was invented by Western Electric in 1940. Other major components are the elastic reeds and magnets or electromagnets that are turned on or off.
After 60 years, the reed switch has been improved to make it more reliable and to reduce the cost while improving the quality. Due to these dramatic improvements, the reed switch has become the design choice in some demanding applications where quality, reliability and safety are paramount.
The most noticeable application for the quality and reliability of the reed sensor is in automatic test equipment (ATE). Technology is first class in this kind of equipment. Reed switches are used for reed relays, which are used in ICs, ASICs, silicon test equipment, and printed board test equipment as switches. In these applications, the number of reed relays in a test system may reach 20,000.
The failure rate of a relay is set to 50ppm, so to meet this requirement, the reed relay quality level is much better than the 50ppm requirement. To date, no electromechanical device has ever been heard to have such a level of quality. Similarly, it also applies to some semiconductor devices.
Once in addition to the initial job quality test, the reed switch needs to perform its job well during its lifetime. At this point they have proven to outperform all other switching devices. This is because in many cases, ATE works 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and its cost is the most important. Therefore, the working life of the reed relay needs millions of times.
Another example that facilitates reed relays is its use as a gas sensor, in which it passes time tests in harsh safety applications. The reed sensor is widely used in many demanding automotive safety equipment (such as the height of sensitive brake fluid), and it is used in many medical instruments. This includes cautery equipment, pacemakers and other medical electronic equipment, etc. The reed switch relay isolates small leakage currents.
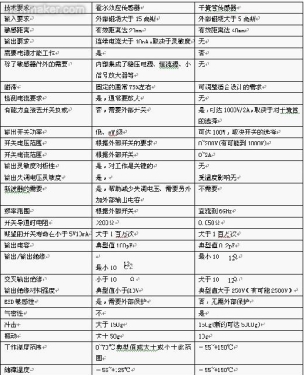
Comparison of reed sensor and Hall-effect sensor In the technology of both the reed switch and Hall-effect sensor, their size is shrinking. However, when the reed switch sensor is compared with a Hall-effect sensor (see the attached table), some advantages of the reed switch can be seen:
1, Hall-effect devices generally have low prices, but they need to be supplied with expensive power supply circuits. Their output signals are also so low, and amplifier circuits are usually added. It can be considered that the final result is that the Hall effect sensor is more expensive than the reed sensor.
2. The reed switch has excellent insulation from the input to the output and the insulation resistance of the switch is up to 10Ω. The result is a leakage current of 10 A. Inserting a human body's probe or pacemaker into a medical electronic device requires that these devices not have any leakage current close to the heart. This is very important. Micro-ampere or sub-microampere currents can change the heart's key electrical activity.
3. The reed sensor is sealed so that it can work in almost any environment (such as no effect on temperature).
4. Reed switch contacts have extremely low on-resistance at turn-on, typical values ​​as low as 50mΩ, and Hall effect sensors may have hundreds of ohms.
5. The reed sensor can directly switch the signal range from a few nanovolts to kilovolts, and the current is from flying safety to safety, and the frequency is from DC to 6GHz. The output range of a Hall-effect device is very limited.
Reed sensors provide a large range of magnetic sensitivity.
7. Reed sensors are insensitive to ESD, and ESD can often damage Hall effect sensors.
8. The reed sensor can withstand very high voltages (minimum rating is 1000V). Hall-effect devices require an external circuit rated to 100V.
9. The reed sensor can withstand a typical 3-foot drop test. The drop test is similar to a Hall effect sensor.
10. Because the reed sensor has no wear components, the low-level load (less than 5V at 10mA and below) can work up to a million times. This corresponds to the number of semiconductor microfabrication devices.
11. The reed switch sensor has no effect on the temperature environment. The typical operating temperature range is from -50°C to +150°C, with no special conditions, limitations or costs. Hall effect sensors have limited operating temperature range.
Reed switch products have many good applications. Some reed switch relay plants are excellent for designing demanding applications, and are superior in quality, reliability, and safety.
China leading manufacturers and suppliers of Wooden Hanging Lamp,Wooden Pendant Light, and we are specialize in Wooden Ceiling Light,Modern Wood Pendant Light, etc.
the types of lamps include pendant lamps, table & floor lamps, chandelier, Wall Lamp ,desk lamp and etc., the materials include steel, metal, fabric, crystal, glass, aryclic and so on.
We offer samples with new designs every month to update our showroom and well display in lighting exihibtions.
We can make samples for his own designs as per shop drawings even potential idea from customers.
Wooden Pendant Light
Wooden Hanging Lamp,Wooden Pendant Light,Wooden Ceiling Light,Modern Wood Pendant Light
Monike lighting , https://www.monikelight.com