Yesterday, someone asked Xiao Bian to think about whether or not to purchase a notebook after the holiday. Whether the timing is appropriate, Xiao Bian feels that I can just use this question to tell you about it. In March 2018, Intel launched its 8th generation Core Duo processor, focusing on notebook performance with new notebook models hitting the market. Before the 8th generation Core Duo, there were U-series low-voltage CPUs.

What's New in the 8th Generation Core Duo?
According to recent reports, the 8th generation of Core Duo notebooks includes models like Core i5-8300H, i5-8400H, i7-8750H, i7-8850H, i9-8950HK, Xeon E2176M, and E2186M — a total of seven models. These CPUs are expected to outperform their 7th generation predecessors significantly.
The new i5s are designed for standard power usage, but they differ from desktop counterparts. While desktop i5s have 6 cores and 6 threads, the notebook version uses a 4-core, 8-thread design to manage power consumption better. Despite lower base clock speeds, these processors feature higher Turbo frequencies and an 8MB L3 cache, which is a big improvement over previous generations.
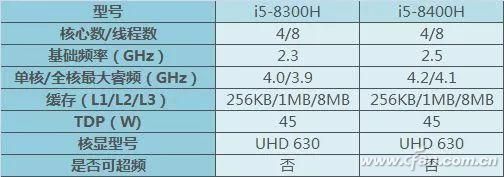
The 8th generation i7s are similar to their desktop versions, featuring 6 cores and 12 threads. However, their base clock speed is reduced compared to the previous generation. The L3 cache has also increased to 8MB, making them more efficient. Still, the TDP remains at 45W, which suggests that even with 14nm process improvements, managing heat is still a challenge.
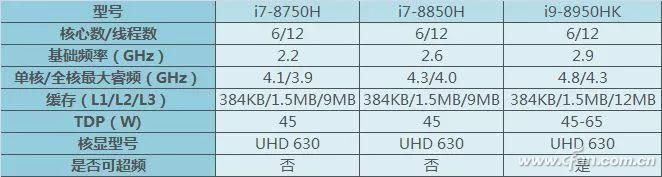
Intel also introduced the i9 series for laptops, which is different from the desktop i9. These are essentially overclockable mobile i7s without a lock, allowing for higher power consumption (45W to 65W). They are likely intended for high-end gaming laptops and professional workstations.
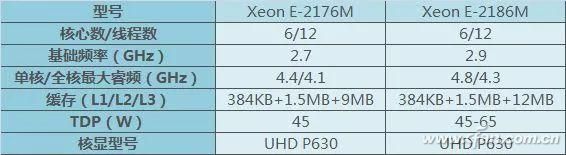
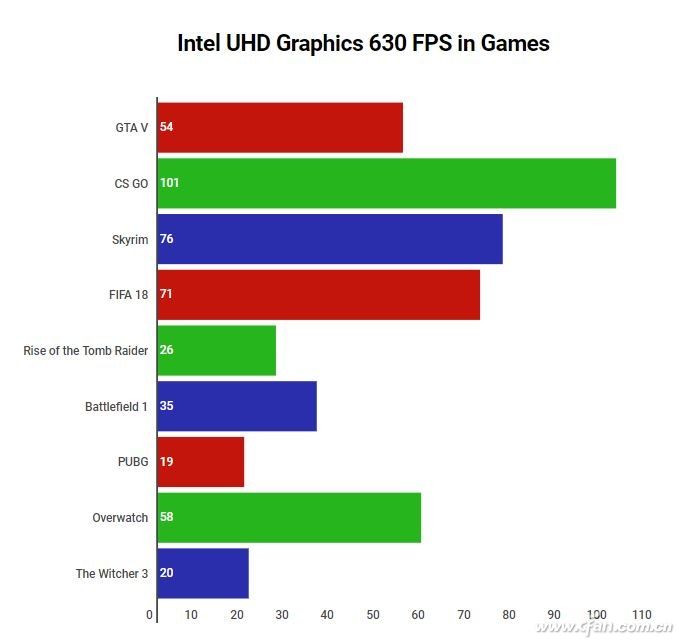
There are also Xeon models aimed at mobile workstations, designed for professionals. These are not for general users. All 8th-gen Core CPUs come with UHD 630 integrated graphics, which handles 4K well and performs similarly to the P630 variant.
Will the Power Wall Be a Major Problem?
Despite the 14nm process, the 8th-gen Core CPUs still face power wall challenges. More cores mean more heat, so Intel had to reduce base clock speeds and increase Turbo frequencies to compensate. Additionally, larger caches improve efficiency at lower frequencies.
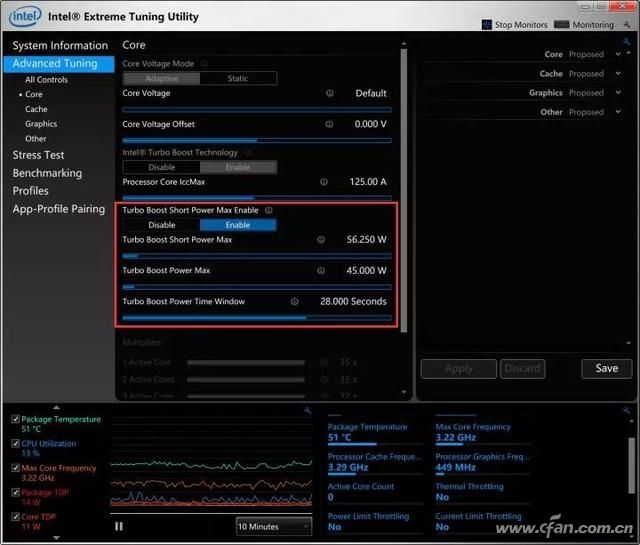
However, if a laptop doesn't have a good thermal design, running the CPU at full load for long periods is difficult. This means manufacturers need to update cooling systems. If they don’t, users might hit the power wall, leading to performance throttling. So, be cautious when buying a system with the 8th-gen Core.
Buying Tips
If you're considering the 8th-gen Core CPUs, here are some suggestions:
- The new i5s offer great performance, almost matching the i7-7700HQ. For most users, the i5 should be sufficient.
- Avoid 7th-gen Core CPUs now — they’re outdated and will soon be obsolete.
- Don’t buy older models with the new CPU. Poor thermal design could lead to overheating and performance issues.

Engine drive Pump:
. Pump driven by diesel engine directly
. Pump driven by gas engine directly
. Water pump stantion
. Oil pump station
Engine Pump,Gas Engine Pump,Engine Driven Pump,Diesel Engine Pump
Guangdong Superwatt Power Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.swtgenset.com