Silicon (Si)-based anode materials are highly promising for lithium-ion batteries due to their high theoretical specific capacity of 4200 mAh/g. However, during the charge and discharge cycles, silicon undergoes a volume change of over 300%, which generates significant internal stress. This stress often leads to electrode cracking, particle detachment, and ultimately, poor cycle stability. As a result, finding suitable binders that can accommodate such large volume changes is crucial for enhancing the performance of silicon-based anodes.
In lithium-ion batteries, the binder plays a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity of the electrode. Binders can be broadly categorized into oily binders, which use organic solvents as dispersants, and aqueous binders, which rely on water. While PVDF has been widely used as an oily binder, it exhibits limited electrochemical stability and weak interaction with silicon particles, making it unsuitable for long-term cycling. Researchers have explored modifications to PVDF, such as copolymerization and heat treatment, to improve its performance. For instance, terpolymers like P(VDF-TFE-E) have shown enhanced mechanical properties, while heat-treated PVDF demonstrated improved viscoelasticity and cycle performance.
Aqueous binders, such as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), polyacrylic acid (PAA), and sodium alginate, have gained attention due to their environmental friendliness and cost-effectiveness. CMC, in particular, forms strong chemical bonds with silicon and helps in the formation of a stable solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) film. Studies have shown that CMC/Si electrodes can achieve high capacities and good cycle stability under optimized conditions. However, factors like pH, substitution degree, and electrode composition significantly affect performance.
PAA, with its ability to form uniform coatings and strong hydrogen bonding with silicon, has shown excellent results in improving cycle life. Sodium alginate, similar to CMC, also performs well but suffers from high hydrophilicity. Conductive polymer binders, such as polyaniline and poly(9,9-dioctylfluorene-co-fluorenone-co-methylbenzoic acid), offer both adhesion and electrical conductivity, further enhancing the performance of silicon-based anodes.
Other binders like carboxymethyl chitosan, polyacrylonitrile (PAN), and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) also show promise, though their performance tends to be slightly lower than that of CMC, PAA, or sodium alginate. Overall, the development of aqueous binders that can form strong chemical bonds and uniform coatings with silicon remains a key area of research. Additionally, conductive polymers with both adhesive and conductive properties are expected to play a significant role in future advancements of silicon-based anode materials.
Solar Engergy System
Solar energy system, off gird pv system, grid pv system, solar power system, Solar Panel system, on grid solar system, grid tied solar system,20kw solar system
Solar energy system include Solar photovoltaic system: 1. Off grid photovoltaic system mainly consists of solar modules, controllers, and batteries. To supply power to AC loads, it is also necessary to configure an AC inverter. 2. Grid connected photovoltaic power generation system. 3. Distributed photovoltaic power generation system. Distributed power generation or distributed energy supply.
|
solar cell type
|
mono crystalline, half cut cell
|
|
solar energy pv system include
|
on grid system, off grid system, hybrid system
|
|
solar configuration
|
solar panel, inverter, battery, bracket cabels, mc4 connector
|
|
|
Product details and pic
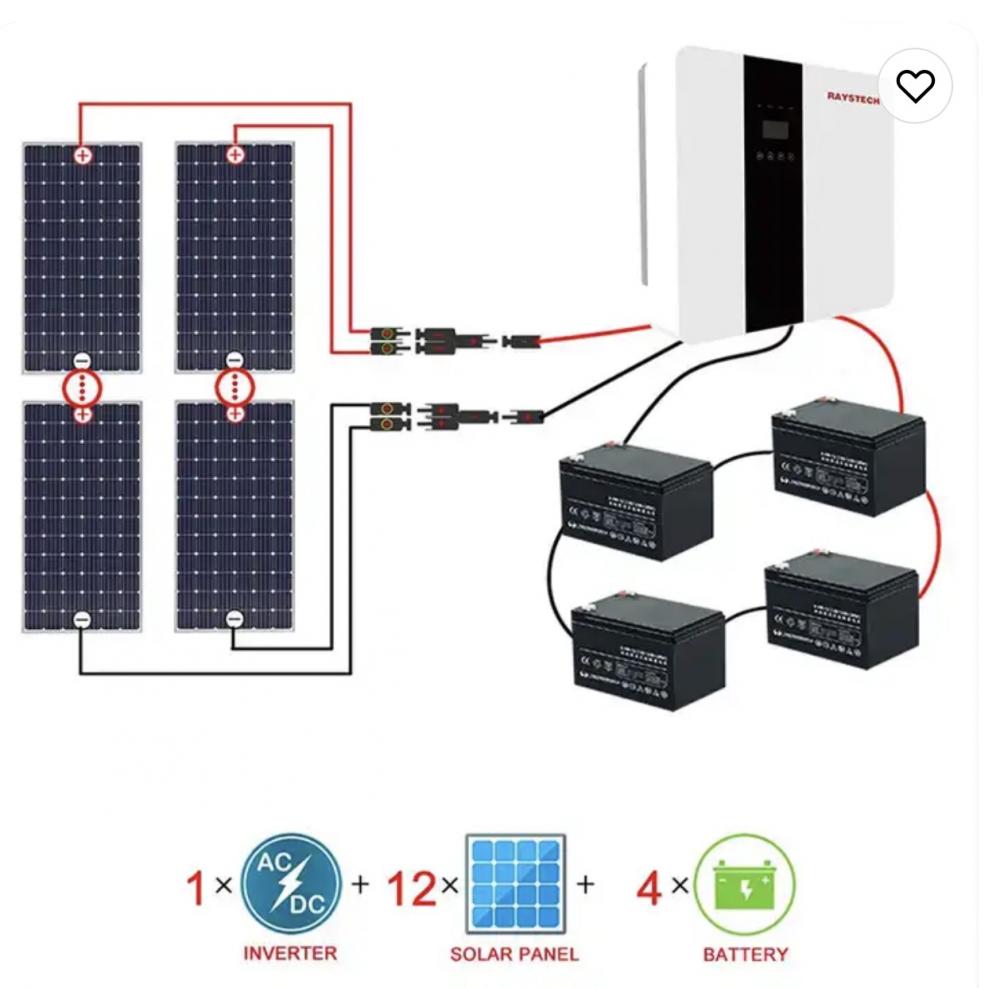

Solar Engergy System,Gird Solar Power System,Pv System For Carport,Energy System Off Grid Solar System
PLIER(Suzhou) Photovoltaic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pliersolar.com

