Many small partners are confused about the difference between relay interlock control and PLC control, as they share a lot of similarities. Today, we’ll explore the relationship between the two and explain how they work differently.
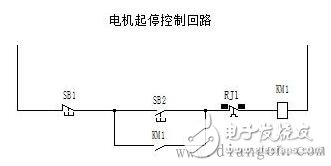
If you compare the relay logic control circuit with the PLC control system, you’ll notice that they function in distinct ways. In a relay-based interlock system, such as the one shown in Figure 1, if there are multiple control loops, any start or stop button press will immediately activate or deactivate the corresponding contactor. For simplicity, we’re ignoring the time it takes for the contactor to energize or de-energize. In essence, this is a parallel process. If we think in computer terms, the system is always "interrupting" — meaning that any input action is responded to instantly.
Now consider the PLC control system shown in Figure 2. This operates according to a program like Program 1. The process works as follows: first, inputs are read, then latched, followed by a scan of the program from top to bottom and left to right. After processing, the results are latched and output. This is driven by a clock signal and runs sequentially — input, program execution, output, and then repeats. Although the scan happens very quickly, we don’t perceive it because of the speed. In most cases, outputs are continuously refreshed unless specific interrupt routines are used.
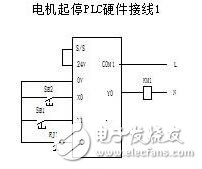
The key difference lies in their operation methods. Not all input signals can be reliably captured by a PLC. For instance, high-frequency signals like those from a counter may not be fully processed by a standard PLC input. In such cases, you need to use a high-speed counter interface and a dedicated high-speed counter module. However, for regular input signals, a PLC is more than capable. For example, when using an FX2 PLC with a 1K program, and pressing an IDEC brand start button, the PLC consistently recognizes the input even if the button is pressed briefly. This shows that although the PLC processes information in a "serial" manner, its speed is so fast that it effectively captures all normal inputs.
Therefore, while PLCs operate sequentially, their speed is sufficient for most applications. Special interfaces and instructions are needed only for specific tasks, such as high-speed counting. For general control, a well-designed PLC program should perform flawlessly. Just make sure you're aware of the limitations and choose the right components for your application.
Digital Signage Player,Electronic Signage,Signage For Hotels,Commercial Digital Signage Displays
Guangdong Elieken Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.elieken.com